But he was also one of the great linguists of the 19th century. Indo -European languages diffused across Europe. The third one is East Germanic , which is now extinct.
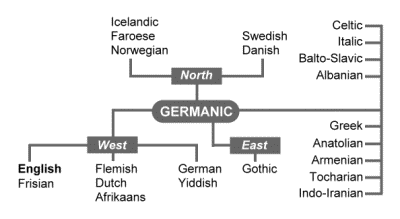
English language is part of the West. Specifically, the West Germanic branch. Branches of Indo-European Languages.
This branch of languages was predominant in the Asian portion of Turkey and some areas in northern Syria. I will describe each of these branches separately. The languages originated in Central Europe and once dominated Western Europe (around 400BC). In the family tree provided below, the languages in the bottom boxes are the largest member language(s) of their respective branches.

Celtic branch of the Indo. In the early nineteenth century, language historians identified German as a member of the Germanic subfamily of the Indo-European family of languages. Written Persian is transcribed by a modified version of Arabic script, even though Persian is a member of the Indo-European family of languages. It antedates the earliest written records of the family and is reconstructed by philologists in the same way as is the parent Indo-European.
Cornish and Welsh were not known to be part of the Indo- Germanic family. Some linguists also believe that the Ainu language of northern Japan is (distantly) related to Indo-European languages. One third of the vocabulary of the Germanic languages is not of Indo-European origin. The stress of words is primarily on the first syllable, and several vowel shifts separate the Germanic languages from other Indo-European languages.
Germanic languages are considered a subdivision of the Indo-European language family , which consists of a total of subdivisions and hundreds of languages and dialects. The Indo-Iranian languages , Indo. Although Germanic languages are spoken across the worl they are primarily concentrated in the majority of Europe (with the exception of the Eastern regions), North America. Because languages cannot be sealed in a vacuum, the parallel branches of the Western Indo-European family have obviously not stayed pure and exclusive.
Latin borrowed extensively from Greek over a period of many centuries. The branch of Indo-European we are most interested in is Germanic (although the Hellenic-Greek branch and Italic-Latin branch , which gave rise to the Romance languages , also became important later). The Germanic , or Proto- Germanic , language group can be traced back to the region between the Elbe river in modern Germany and southern Sweden some.

It also includes Persian and Hindi dialects. There are contradictory theories as to how the language came about but research shows that it was first spoken by a community people who lived approximately. By the 19th century, August Schleicher’s Family Tree had been proposed to model the relationships among the Indo-European languages as the branches of a tree.
The picture below shows how the Indo European Language Family tree branch comes from the main mother tongue trunk. Introduction: Dutch is part of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European language family. Dutch is spoken as a mother tongue by about million people in the Netherlands, parts of Belgium and in the former Dutch colonies. Frisian is a language spoken by approximately half a million people in the Dutch province of Frieslan in nearby areas of Germany, and on a few islands in the North Sea. It is believed that most of the early Germanic peoples used Germanic languages.
Modern scholars, such as historians, archaeologists.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.